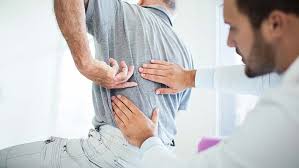
Stress is a common phenomenon in our fast-paced lives. It affects not just our mental health but also manifests in various physical ailments. One such physical condition that is often overlooked but significantly impacted by stress is back pain. Understanding the relationship between stress and back pain is crucial for developing effective management strategies.
Tapentadol is the main active ingredient of Aspadol 100mg, which is nothing more than a film-coated tablet. It is a prescription medicine used to treat opioid pain. This medication can quickly help you feel better if you’re experiencing moderate to severe pain.
The Connection Between Stress and Back Pain
Stress triggers a series of physiological responses in the body, collectively known as the fight-or-flight response. This response involves the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones prepare the body to deal with perceived threats by increasing heart rate, tightening muscles, and boosting energy supplies. While these reactions are beneficial in short bursts, chronic stress can lead to prolonged muscle tension, particularly in the back and neck.
Physiological Impact of Stress on the Muscles
When we experience stress, our muscles tense up as a protective mechanism. This muscle tension is often concentrated in the back, neck, and shoulders, leading to discomfort and pain. Over time, persistent muscle tension can result in:
- Muscle Strain: Continuous muscle tension can cause muscle strains, which are characterized by pain, stiffness, and limited mobility.
- Reduced Blood Flow: Tense muscles restrict blood flow, depriving the muscles of oxygen and essential nutrients, which can exacerbate pain.
- Nerve Compression: Prolonged muscle tension can compress the nerves in the back, leading to nerve pain or sciatica.
Stress and Posture
Stress often affects our posture, leading to poor alignment and additional strain on the back muscles. People under stress may adopt a hunched posture, slouch, or engage in repetitive, tension-inducing behaviors such as clenching the jaw or tensing the shoulders. Poor posture can cause:
- Spinal Misalignment: Incorrect posture over time can lead to misalignment of the spine, resulting in chronic back pain.
- Disc Problems: Slouching or hunching can put excessive pressure on the intervertebral discs, increasing the risk of herniated or bulging discs.
Psychological Factors Linking Stress and Back Pain
Psychological stress not only affects the muscles but also influences how we perceive and react to pain. Stress can:
- Lower Pain Threshold: Chronic stress can lower the pain threshold, making individuals more sensitive to pain.
- Increase Pain Perception: Stress and anxiety can amplify the perception of pain, making minor discomforts feel more severe.
- Cause Sleep Disturbances: Stress often leads to poor sleep quality, which can impair the body’s ability to repair and heal, exacerbating back pain.
It is a member of the class of medications known as analgesics, which act as both an agonist of the mu-opioid receptor and a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor. It is prescribed in tablet form as well as an extended-release form in critical cases if no other medication works. The Aspadol 150mg medication is renowned for its quick pain relief capabilities.
Emotional Impact
Stress and emotional distress can create a vicious cycle where pain leads to more stress, and increased stress leads to more pain. This cycle can result in:
- Chronic Pain: Persistent stress and poor pain management can transform acute pain into chronic pain.
- Depression and Anxiety: Chronic back pain can contribute to mental health issues, which in turn can worsen pain perception.
How to Manage Stress-Related Back Pain
Effective management of stress-related back pain requires a holistic approach that addresses both the physical and psychological aspects of stress. Here are some strategies:
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular physical activity helps to reduce stress and alleviate muscle tension. Exercise promotes the release of endorphins, the body’s natural painkillers, and improves overall physical health. Activities such as yoga, Pilates, and tai chi are particularly beneficial for back pain as they focus on flexibility, strength, and relaxation.
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Mindfulness practices such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation can help reduce stress levels and muscle tension. These techniques promote relaxation and help break the cycle of stress and pain.
Ergonomic Adjustments
Making ergonomic adjustments at work and home can significantly reduce back pain. Ensure that your workspace is set up to promote good posture. Use ergonomic chairs, desks, and computer setups to avoid straining your back.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can be highly effective in managing back pain. A physical therapist can provide personalized exercises and treatments to strengthen the back muscles, improve posture, and reduce pain.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can mitigate the impact of stress on the body. This includes:
- Balanced Diet: Eating a nutritious diet supports overall health and helps the body cope with stress.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensuring sufficient and quality sleep aids in stress management and recovery from back pain.
- Hydration: Staying hydrated is crucial for muscle function and overall health.
Professional Help
Seeking professional help from a psychologist or counselor can be beneficial in managing stress. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and other therapeutic techniques can help individuals develop coping strategies to handle stress effectively.
Conclusion
The intricate connection between stress and back pain underscores the importance of addressing both physical and psychological aspects of health. By understanding how stress affects the body, particularly the back, individuals can adopt effective strategies to manage and alleviate pain. Incorporating regular exercise, mindfulness practices, ergonomic adjustments, and seeking professional help when needed can significantly improve quality of life and reduce the burden of stress-related back pain.